The age of consent, while it has no concrete legal definition, is widely understood to mean the lowest age at which a person is legally competent to give consent to sexual activity with another person. However, the exact definition varies from country to country, and there are other factors that can may make an otherwise illegal sexual act permissible (or vice versa).
The most important one is the so-called close-in-age exemption, also referred to as Romeo and Juliet laws. In some countries, it is legal for a person to have sex with a person under the age of consent provided that the older person is not significantly older than the younger person (usually by no more than 3 years).
In many countries, it is illegal for a person in a position of trust to have sex with a minor (a person under 18). This would apply, for example, to a teacher and his/her student, a child and a foster parent, etc. You can see the ages of consent and possible exceptions to the rules on the map below:
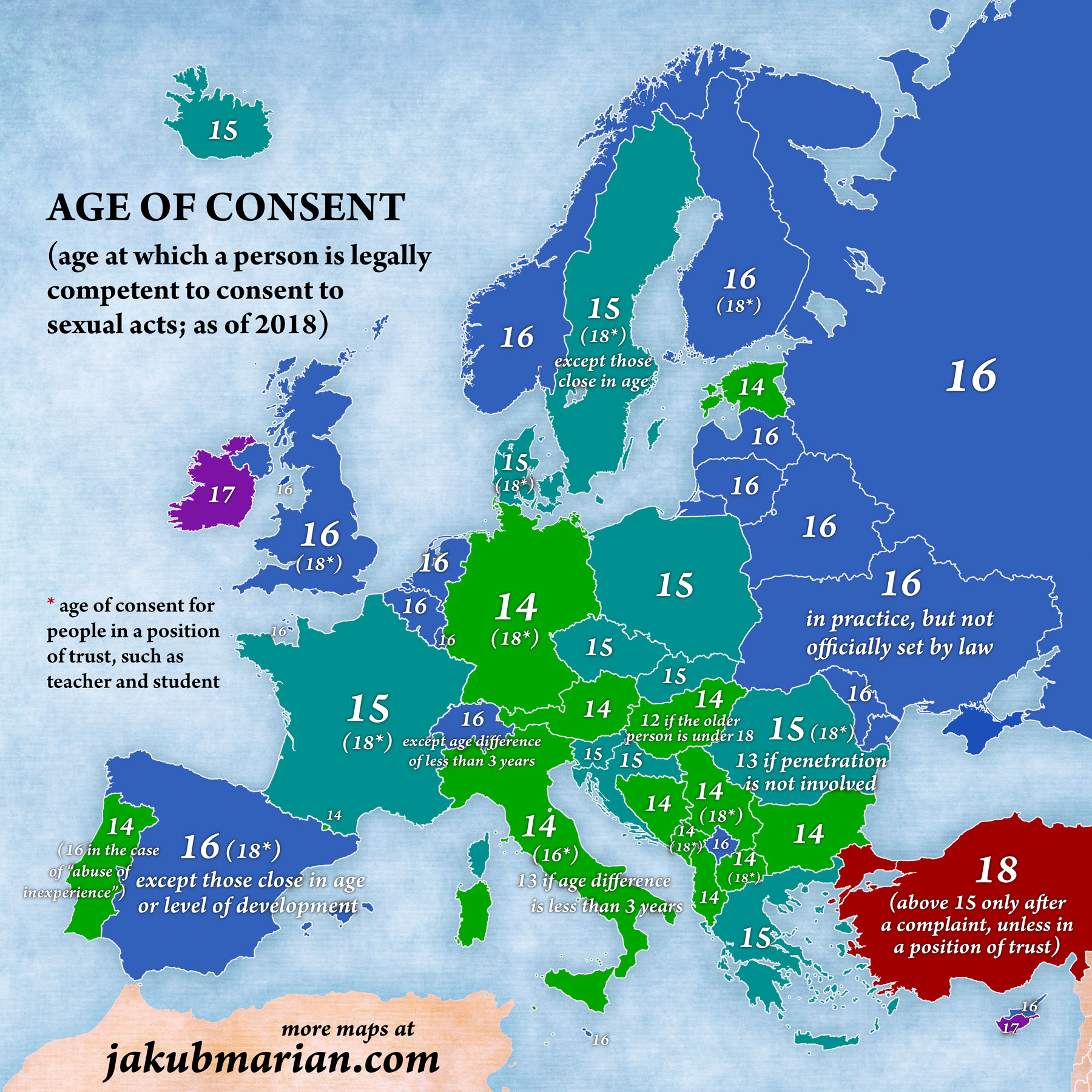
Please note that the colour scheme does not imply that lower numbers (green) are “better” than higher numbers (red), but rather that lower numbers are less restrictive (it is harder to break the law).
To summarize, here are the ages of consent of European countries, including microstates not shown in the map:
| Age | Countries |
|---|---|
| 14 | Albania, Andorra, Austria, Bulgaria, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Estonia, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Liechtenstein, Macedonia, Montenegro, Portugal, San Marino, Serbia |
| 15 | Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Greece, Iceland, Monaco, Poland, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Sweden |
| 16 | Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Belgium, Finland, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kosovo, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Moldova, Netherlands, Northern Cyprus, Norway, Russia, Spain, Switzerland, Ukraine, United Kingdom |
| 17 | Cyprus, Ireland |
| 18 | Turkey, Vatican City |
 Tip: Are you a non-native English speaker? I have just finished creating a
Tip: Are you a non-native English speaker? I have just finished creating a  Web App
Web App