The OECD provides data on the average class size of European countries in primary and lower secondary education. The OECD defines the value as the total number of students divided by the total number of classes (in the respective level of education), excluding special education. This should not be confused with the pupil–teacher ratio.
The average class sizes in primary education are as follows:
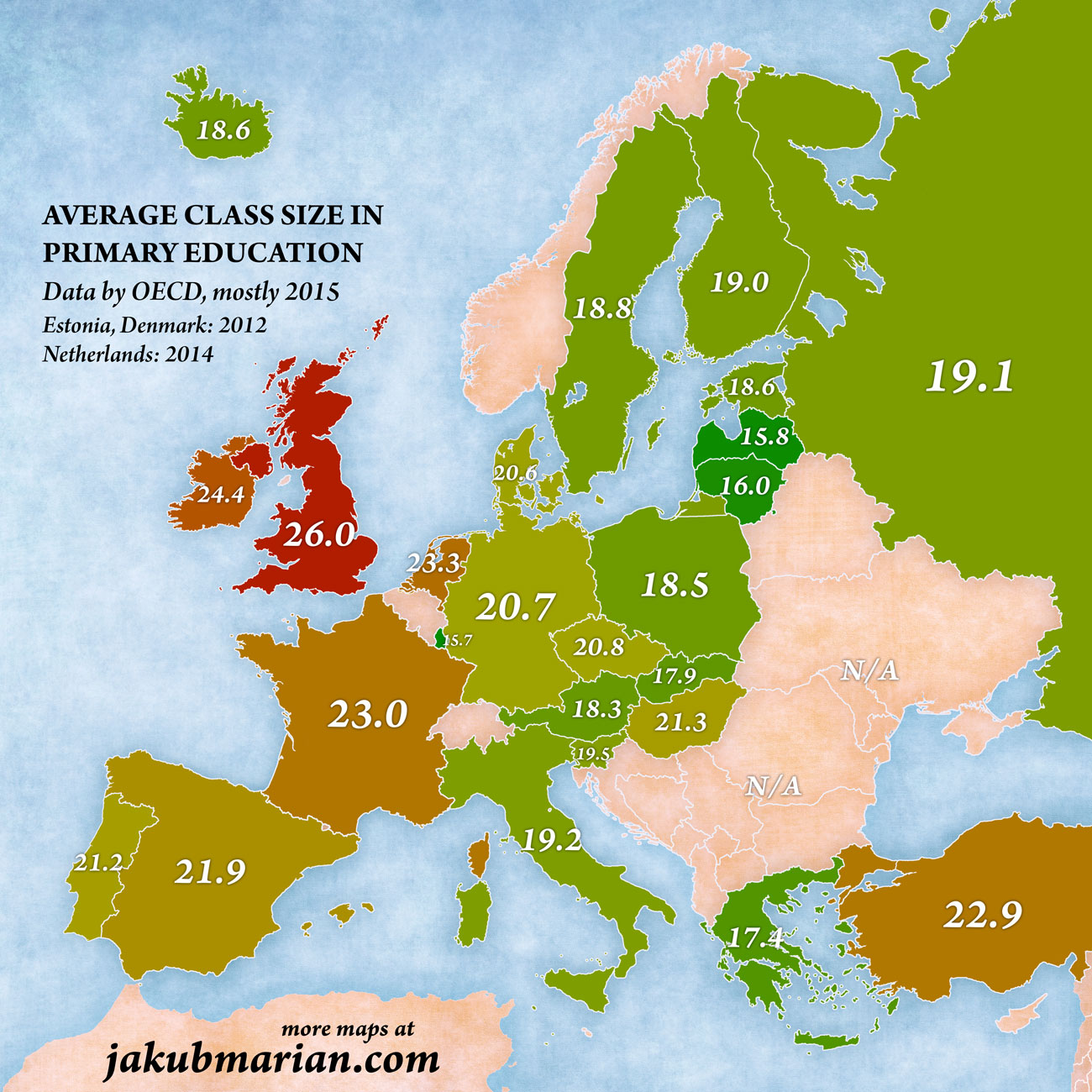
For comparison, here are the corresponding sizes in other countries: United States 21.1, Brazil 23.0, India 23.5, Japan 27.3, China 37.5.
The figures look significantly different in lower secondary education:
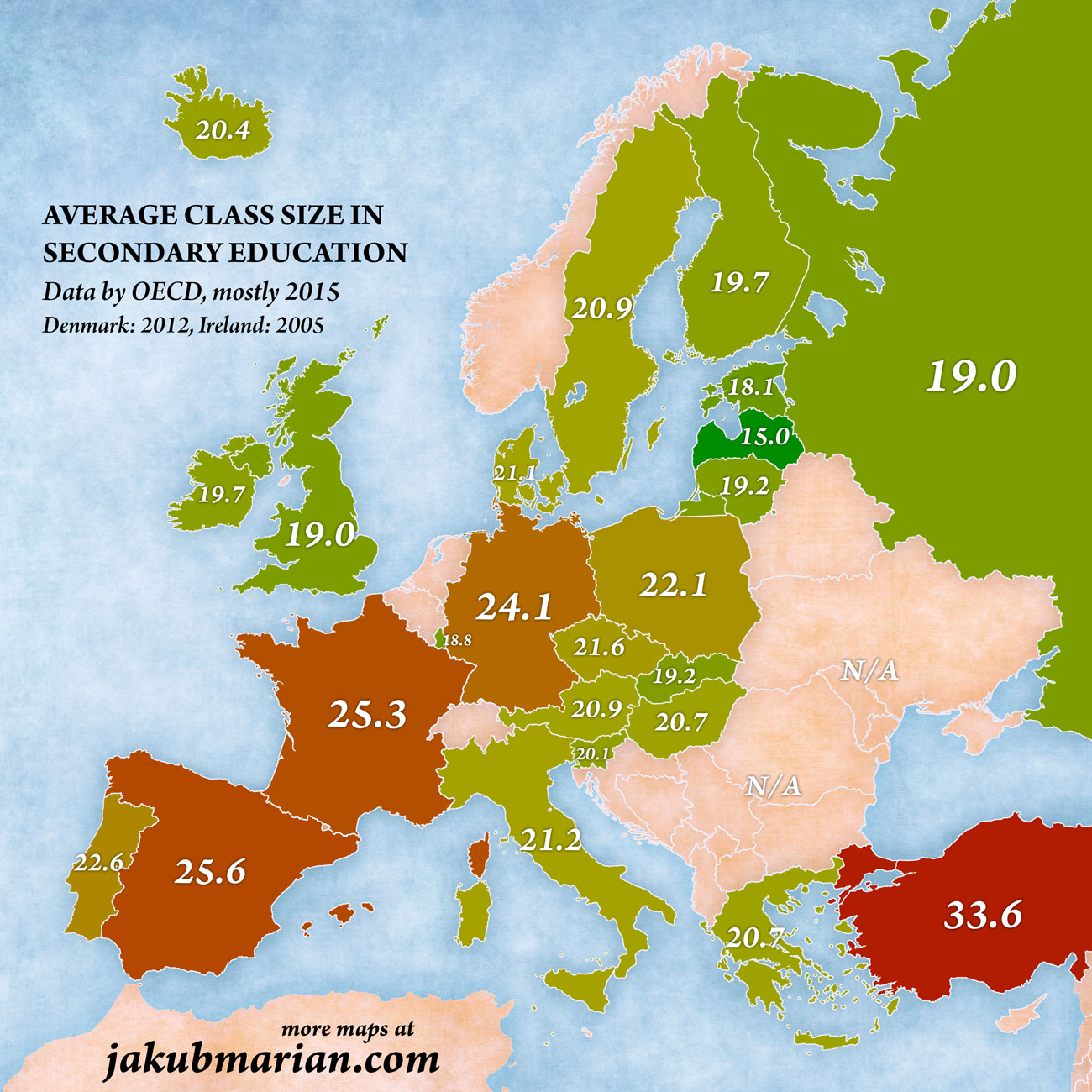
For comparison: India 22.4, United States 26.7, Brazil 27.0, Japan 32.3, China 48.8.
There are more students, on average, in a class in lower secondary education than in primary education in most countries, except Estonia, Hungary, Ireland, Latvia, the United Kingdom, and Russia (and India).
 Tip: Are you a non-native English speaker? I have just finished creating a
Tip: Are you a non-native English speaker? I have just finished creating a  Web App
Web App